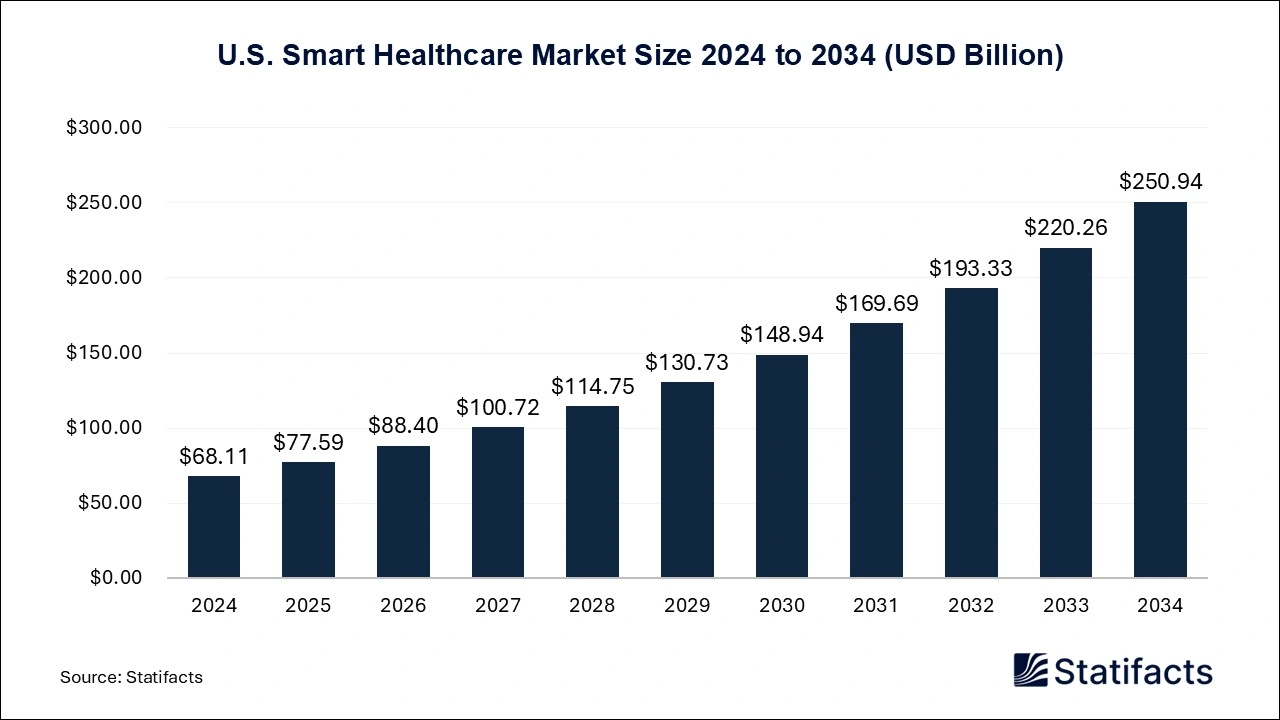
The U.S. smart healthcare market size is calculated at USD 68.11 billion in 2024 and is predicted to reach around USD 250.94 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 13.93% from 2025 to 2034.
U.S. Smart Healthcare Market Report Highlights
- By product type, the mHealth product segment dominated the market and accounted for the highest revenue share in 2024.
- By product type, the RFID Kaban system product is expected to be the fastest-growing segment during the forecast period.
- By product type, the telemedicine product segment accounted for the second fastest-growing in the U.S. smart healthcare market.
The U.S. smart healthcare market refers to the production, distribution, and application of smart healthcare and refers to the use of technologies like big data, IoT, AI, and ML to enhance the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery. It involves the integration of many digital technologies and devices to allow the collection, analysis, and sharing of healthcare data. Smart healthcare is a system of healthcare services that uses technology and medical devices such as IoT, wearables, and smartphones to access information. These innovative technologies help comprehensively transform the traditional healthcare system, making patient care more practical, personalized, and convenient.
Major changes in smart healthcare include prevention and treatment models, from centralized management to personalized management, clinical data digitalization, healthcare data digitalization, disease-centered care, and patient-centered care. In addition, a modern healthcare system is considered to fully promote healthcare interactions, ensuring that participants receive the services that they require. It helps organizations and healthcare professionals make accurate decisions and allocate resources rationally.
IoT devices are transforming healthcare by connecting sensors, medical devices, and other equipment to the internet, allowing predictive maintenance, remote patient monitoring, and real-time monitoring, which helps the growth of the U.S. smart healthcare market. IoT-based healthcare solutions enable healthcare providers to remotely monitor patient’s vital signs, disease progression, and medication adherence, leading to better outcomes and more effective healthcare delivery. At the heart of IoT-based healthcare are sensors that collect and analyze real-time data. These sensors empower healthcare providers to focus on what matters most, spending more time with patients diagnosing and treating conditions while reducing the time on administrative tasks and logistics work.
IoT-based wearable devices, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical alert systems, allow people to track their health and physical activity. By using IoT, the hospital management system with patient health monitoring using RFID tags and many sensors aims at building a better means of storing and retrieving patient data. RFID helps to monitor the status of the patient by tracking all the health services given to patients. IoT benefits for the healthcare industry include data-driven insights and predictive analytics, telemedicine and improved access to care, efficiency and resource management, personalized treatment and chronic disease management, remote patient monitoring, and early disease detection.
Artificial intelligence (AI) technology is leveraged to analyze a high amount of healthcare data, ranging from patient records and medical images to genetic information and sensor data, which contributes to the growth of the U.S. smart healthcare market. AI-based algorithms can identify trends, patterns, and insights that can inform clinical decision-making, personalize treatment plans, and improve diagnostic accuracy. AI could significantly reduce inefficiency in healthcare, enhance patient flow and experience, and improve patient safety through the care pathway. AI can be used to support digital communications, offering schedule reminders, tailored health tips, and suggested next steps to patients. AI is primarily used to increase speed and accuracy in healthcare.
AI algorithms can analyze medical imaging data, such as CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays, to assist healthcare professionals in swift and accurate diagnoses. Imaging software is one of the most commonly used applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare. AI-based imaging software can help doctors quickly and accurately identify diseases and disorders and also help plan treatment strategies. The scope of AI in healthcare amplifies diagnostic precision and expedites decision-making processes, facilitating a seamless workflow that ultimately improves patient care outcomes.
Personalized public health interventions are playing an important role in driving the growth of the U.S. smart healthcare market. Personalized health planning is an important feature of personalized health care. It includes the individual’s specific health needs and develops a coordinated means to achieve them. Personalized treatment plans are customized healthcare strategies tailored to an individual’s unique needs, medical history, and preferences. They aim to improve health outcomes by considering specific factors that affect a person’s well-being. In the evolving healthcare landscape, personalized medical devices have emerged as a groundbreaking approach, tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their unique characteristics. These include devices that are personalized or custom-made to be adaptable to the patient’s solutions.
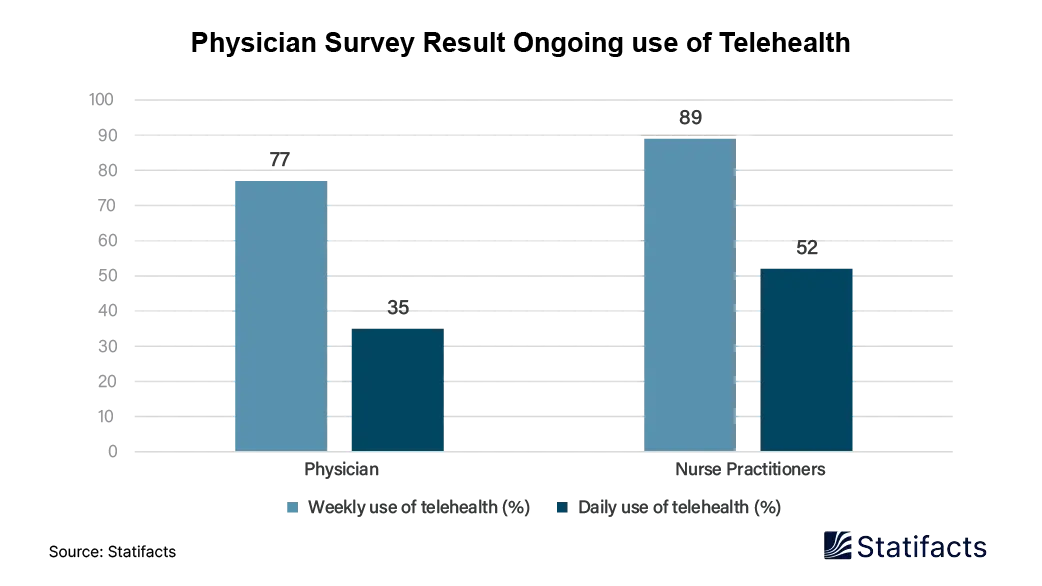
According to a report published in December 2024, a new survey finds U.S. physicians and patients see value in telehealth access, siting medication management, and follow-up visits as the most common reasons for telehealth use. Conducted by digital platform provider Doximity in August and October 2024, the survey polled 1171 U.S. physician telemedicine users across 10 specialties, 131 nurse practitioners, and 2400 adults.
The physician survey results reveal ongoing use of telehealth, with 77% of physician respondents saying they used it weekly and 35% daily. Among nurse practitioners, 89% said they used telehealth weekly, and 52% reported daily use.